BAPO is committed to eliminating discrimination and promoting equality, diversity and inclusion (EDI) in everything we do.
We want to ensure our members and our people are:
- Treated fairly with equality of opportunity and without discrimination.
- Experience a welcoming and inclusive environment that promotes dignity and respect for all.
- Enabled, encouraged and celebrated to contribution to the profession and our work, to represent the diverse backgrounds that make up our profession.
- Protected against bullying, harassment, victimisation and unlawful discrimination.
BAPO aims to:
- Play our part in removing barriers and redressing imbalances caused by inequality and unlawful discrimination. Ensure decisions concerning our members and our people, including recruitment and appointment, are based on merit (apart from any necessary and limited exemptions and exceptions allowed under the Act).
- Review regularly our policies, procedures and working practices to ensure equality, diversity and inclusion are embedded in all we do, to assess our impact and to take account of any changes in the law or good practice.
What is EDI?
EDI stands for equality, diversity and inclusion, other similar acronyms include equity, diversity, inclusion and belonging.
- Equality means ensuring that everyone has the same opportunities and is treated with the same dignity and respect
- Equity means to treat people how THEY want to treated. Equity is the treatment of people according to what they deserve, with an understanding of structural inequalities faced by some people.
- Diversity is about representation and valuing individuals for the different characteristics, perspectives, and experiences they have to offer.
There are two types of diversity:
- Demographic e.g. disability, race, sexual orientation
- Cognitive e.g. people who have different ways of thinking, and different skill sets in a team
- Inclusion is when a person is valued for their uniqueness, it involves positively striving to meet the needs of different people and taking deliberate action to create environments where everyone feels respected and able to achieve their full potential
- Belonging is feeling secure, supported, accepted, and included
Equality Act 2010 ‘the Act’. This is Legislation that applies in England, Wales and Scotland, but not in Northern Ireland. This protects people from discrimination, harassment or victimisation.
Under the Equality Act you are protected from discrimination:
when you are in the workplace
when you use public services like healthcare or education
when you use businesses and other organisations that provide services and goods
when you use transport
when you join a club or association
when you have contact with public bodies like your local council or government departments
The Act sets out a number of what are known as ‘protected characteristics.’
Northern Ireland:
– Gaps in equality law between Great Britain and Northern Ireland (equalityni.org)
– ECNI – Single Equality Act
– ECNI – The Law, Equality Legislation, Equality Commission, Northern Ireland
The equalities act also includes public Sector Equality Duty, whereby public bodies (like local councils, hospitals, and publicly-funded service providers) must consider how their decisions and policies affect people with different protected characteristics. The public body also should have evidence to show how it has done this, so this will be relevant to our profession.
The UN Convention on disability rights has been agreed by the UK to protect and promote the rights of disabled people.
The equality and human rights commission are Britain’s independent equality and human rights regulator. Their role is in enforcing and upholding the laws that safeguard everyone’s right to fairness, dignity and respect. The commission enforces the Equality Act 2010. Homepage | EHRC
The following characteristics are protected characteristics –
- age
- disability
- gender reassignment
- marriage and civil partnership
- pregnancy and maternity
- race and ethnicity
- religion or belief
- sex
- sexual orientation
Areas of note with regards protected characteristics
- Sex is different from gender, sex is a label assigned at birth based on the reproductive organs a person is born with. There are male and female groups and intersexpeople are born with both male and female reproductive organs. Gender involves how a person identifies and can cover a broad spectrum.
- Ethnicity and race are separate and can sometimes be confused. Ethnicity is linked to cultural expression and identification and is defined as large groups of people classed according to common racial, national, tribal, religious, linguistic, or cultural origins or backgrounds. This is different from race which is usually associated with biology and linked with physical characteristics such as skin colour or hair texture and is defined as people who share certain distinctive physical traits.
- Disability discrimination must consider ableism, which is discrimination and social prejudice against people with disabilities or those who are perceived to be disabled.
- Religion includes protection against discrimination for those who do not hold a belief, the equality act notes that religious protections must not be incompatible with human dignity and not in conflict with the fundamental rights of others. For example, beliefs around racial superiority or heteronormative superiority are not protected.
Discrimination – The equalities act 2010 protects people from discrimination, there are a number of different kinds of discrimination, please click on the links to learn more about each type of discrimination:
- Direct discrimination
- Combined discrimination: dual characteristics
- Discrimination arising from disability
- Gender reassignment discrimination: cases of absence from work
- Pregnancy and maternity discrimination: non-work cases
- Pregnancy and maternity discrimination: work cases
- Indirect discrimination
- Indirect discrimination: same disadvantage
Harassment is unwanted behaviour that a person finds offensive, where the other person’s behaviour is because:
- you have a protected characteristic
- there is any connection with a protected characteristic (for example, you are treated as though you have a particular characteristic, even if the other person knows this isn’t true)
Unwanted behaviour could include:
- spoken or written abuse
- offensive emails
- tweets or comments on websites and social media
- images and graffiti
- physical gestures
- facial expressions
- banter that is offensive to you
You don’t need to have previously objected to it.
The unwanted behaviour must have the purpose or effect of violating your dignity, or creating a degrading, humiliating, hostile, intimidating or offensive environment for you.
To be unlawful, the treatment must have happened in one of the situations that are covered by the Equality Act. For example, in the workplace or when you are receiving goods or services.
For more information see https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2010/15/section/26 and Harassment and victimisation | EHRC
Victimisation is treating someone badly because they have done a ‘protected act’, or because an employer, service provider or other organisation believes that a person has done or is going to do a protected act. The reason for the treatment does not need to be linked to a protected characteristic.
A protected act is:
- making a claim or complaint of discrimination (under the Equality Act)
- helping someone else to make a claim by giving evidence or information
- making an allegation that you or someone else has breached the Equality Act
- doing anything else in connection with the Equality Act
See Equality Act 2010 and Harassment and victimisation | EHRC for more details
Health inequalities
- Healthcare inequities are differences in healthcare that are avoidable, unfair and unjust
- Health disparities are differences in health amongst groups of people
What Are Health Inequalities? | The King’s Fund – Article discussing health inequalities and life expectancy
Tackling Health Inequalities | Seven Priorities For The NHS | The King’s Fund – Kings fund project discussing the seven key priorities to tackle health inequalities

Intersectionality
- Considers how human beings differ and how the intersection of those differences creates unique experiences
- Different forms of oppression overlap, creating unique societal and personal consequences of these intersections.
- Intersectionality can impact on health outcomes
See this you tube video on intersectionality for more information What is intersectionality?
Lived Experience And Intersectionality In Health Care | The King’s Fund – Kings fund article discussing lived experience and intersectionality in health care
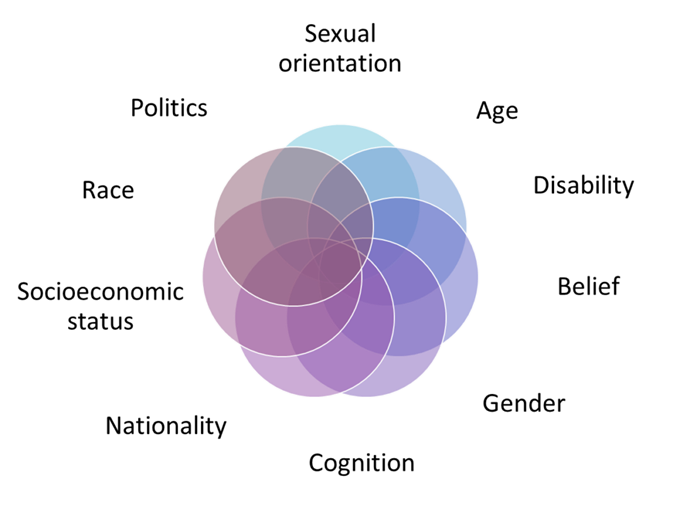

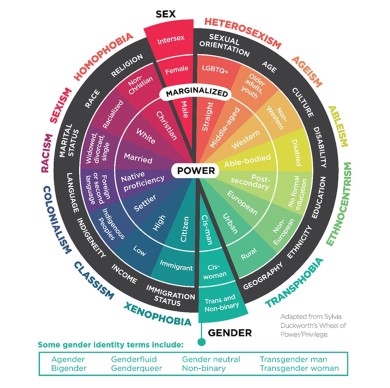
- Privilege is an advantage that an individual or group of people has.
- Privilege can also be an absence of barriers and obstacles that other individuals or groups of people are faced with.
- The wheel of power / privilege considers three factors:
– Individual
– Interpersonal
– Systemic
Those on the inner hub of the wheel you hold the most power and privilege in society whereas those on the outer hub tend to hold the least power and privilege.
- Reflect on where you are on the wheel?
- Reflect on where most other people you know are on the wheel?
- Reflect on where the people on the inner hub and outer spokes of the wheel appear in society?
NHS England » NHS equality, diversity and inclusion (EDI) improvement plan
NHS England » NHS Workforce Race Equality Standard
NHS England » NHS Workforce Race Equality Standard 2023 data analysis report for NHS trusts
NHS England » Workforce Disability Equality Standard
NHS England » Workforce Disability Equality Standard: 2023 data analysis report for NHS trusts
NHS England » Gender pay gap report
CYP_summary_of_final_report_-_accessible.pdf – Care experienced children’s and young peoples summary and recommendations report
HwH International Recruits Review FINAL (1)
DISABILITY
Supporting Disabled staff and learners
health-disability-and-becoming-a-health-and-care-professional.pdf – Information for Disabled learners on becoming a healthcare professional
Understanding disability infographic | NHS Employers – Disability statistics and considerations
How to recruit and support disabled staff in the NHS | NHS Employers – Recruiting and retaining Disabled staff
Understanding and supporting staff with a hidden disability | NHS Employers – Support for staff with hidden disabilities
Health passports
NHS England » Health and care passports – Health passports for patients
https://www.nhsemployers.org/system/files/media/Health-passport_0.pdf – NHS employers health passports for staff
health-adjustment-passport.pdf – Department for Work and Pensions health adjustment passport
About | AXS Passport – Diversity and ability adjustments passport
health-adjustment-passport.pdf
Reasonable adjustments
Neurodiversity
By focussing on the communication needs of patients, and in particular those who may have different requirements in terms of communication style, such as patients with mental health conditions, or neurodiversity such as learning difficulties or autism, can impact upon how effectively the patient then engages with the NHS and social support systems.
Simple changes made in clinic can have a great impact on a patient’s experience. Accessible information, that includes simplified language, imagery and symbols can be helpful in aiding communication. Inclusive communication means to recognise and utilise all forms of communication rather than just written and verbal, such as facial expressions, gestures, movements, signs, pictures, and objects.
![]()
Images from Icons word 365
Click the link below for various case studies on AHP’s transforming the health, care, and wellbeing of neurodiverse patients: ld_autism_case_study_collection_finalv3.pdf (ahpnw.nhs.uk)
Celebrating Neurodiversity – Made in Salford – Ellie studies English and Drama, and Helen is an Adult Nurse Lecturer, both are neurodivergent and are based at the university of Salford. This article documents their reflections on how being neurodivergent impacts their day-to-day lives and the unique strengths that come along with it.
Hidden disabilities
Living with Non-Visible Disabilities – The Disability Unit – Definition of hidden disabilities
Hidden disabilities (hdsunflower.com) – Types of hidden disabilities
A symbol for non-visible disabilities – Information on the sunflower lanyard and hidden disabilities
Disabled student allowance
Health Learners: DSA Find Your Way | D&A | Diversity and Ability – Information for health learners
Help if you’re a student with a learning difficulty, health problem or disability: Disabled Students’ Allowance – GOV.UK – Government information on what DSA is
Disabled Students’ Allowances (DSA) guide 2024 – Save the Student – Article documenting eligibility and signposts to application for DSA
Access to work
Health Professionals: Access to Work Find Your Way | D&A | Diversity and Ability
LGBTQ+
Equality, Diversity and Inclusion (EDI) – BAPO LGBTQ+ pride information
Health-and-Care-LGBTQ+-Inclusion-Framework.pdf (nhsconfed.org) A practical framework for health and care leaders to create inclusive environments for LGBTQ+ staff and patients across six pillars
National LGBT Survey: Research report – GOV.UK – National LGBTQ+ experience survey report
Diabetes – Trans Gap Project (wordpress.com) – Project considering the intersection between trans people and diabetes diagnosis
RACE AND ETHNICITY
https://www.blackandbrownskin.co.uk/mindthegap – Clinical Handbook of signs and symptoms in dark skin tones
Equity in medical devices: independent review – final report – GOV.UK – Findings and recommendations of the independent review into racial, ethnic and other factors leading to unfair biases in the design and use of medical devices
The Health Of People From Ethnic Minority Groups In England | The King’s Fund – Article discussing health inequalities, experiences and outcomes for different ethnic groups
A scoping review exploring the confidence of healthcare professionals in assessing all skin tones – PMC – Scoping review of health care professional confidence of assessing different skin tones
Our Strategy – NHS – Race and Health Observatory – The NHS Race & Health Observatory strategy 2021– 2024: Driving Race Equity In Health and Care
Adult obesity and type 2 diabetes – Public health England report into adult obesity and type 2 diabetes
191ac9b79f47de2896cf1a30f39037f5.pdf – Addressing skin tone bias in wound care
Ethnic inequalities in hospital admissions in England: an observational study | BMC Public Health | Full Text – Observational study of ethnic inequalities in hospital admissions in England
THE REFRAME IMAGE LIBRARY
The Reframe image library is a diverse and inclusive collection designed to increase visibility of under-represented groups in healthcare images:
https://reframeimagelibrary.fotoware.cloud/fotoweb/
BAPO Response to riots

BAPO would like to extend support and solidarity to anyone affected by the current violence that we are seeing reported. BAPO strongly condemns the violent and racist riots and intimidation that have taken place across the country. We value diversity, it is the cornerstone of our profession and of course, the wider NHS and companies that support the profession. During challenging times like these, we need to demonstrate our values of community, inclusion and allyship more than ever. We encourage members to stand together to support any staff, service users or members of the public affected. We understand that current events may create feelings of fear, distress and anxiety, the following collated signposting and support links might be helpful.
Wellbeing support for Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic NHS staff (hee.nhs.uk) provides links for support services offered to NHS colleagues from culture and ethnically diverse backgrounds
Black Minds Matter’s connects Black individuals and families with free mental health services by professional Black therapists to support their mental health.
The Black, African and Asian Therapy Network BAATN is the UK’s largest independent organisation to specialise in working psychologically, informed by an understanding of intersectionality, with people who identify as Black, African, South Asian and Caribbean.
Taraki work with Punjabi communities to improve access to mental health awareness, education, social supports, and research through culturally safe activities to benefit individual and community-level care.
The National Union of Students (NUS) Black students’ network represents students of African, Asian, Arab and Caribbean heritage. The network supports issues affecting Black students on a local, national and international level.
Nafsiyat is a pioneering charity offering intercultural therapy in over 20 languages to people from diverse cultural communities. Nafsiyat offers short-term intercultural therapy to people from diverse backgrounds who live in Islington, Enfield, Camden and Haringey.
Nilaari is a Black, Asian and Ethnically diverse led community-based charity. Their diverse staff team deliver culturally appropriate and responsive social care support and talking therapies. All services are designed to support client’s emotional wellbeing and mental health. Nilaari provides community-based mental health care for people living in Bath and North East Somerset (B&NES), Bristol, North Somerset, South Gloucestershire, Swindon and Wiltshire.
BMHS Wales is a not-for-profit organisation focused on education and advocacy to inspire mentally healthy ethnically diverse communities by providing support appropriate to their mental health and wellbeing.
Saheliya (Edinburgh and Glasgow) Saheliya is a specialist mental health and well-being support organisation for black, minority ethnic, asylum seeker, refugee and migrant women and girls (12+) in the Edinburgh and Glasgow area. Their staff are from a variety of different cultures and ethnic backgrounds and they all have an understanding of how race, gender and culture affects the mental well-being of black and minority ethnic women and girls.
If you have any feedback or need any support from BAPO to further support colleagues and communities affected by this, please email : enquiries@bapo.com
- https://youtu.be/qetaR5oeb6s?feature=shared Black history month
- https://youtu.be/WbFZvlcwqt4?feature=shared Disability
- https://youtu.be/G3Aweo-74kY?feature=shared Gender roles
- https://youtu.be/Q1D65SxzojI?feature=shared LGBTQ+
- https://youtu.be/xsfml3yVh1g?feature=shared Neurodiversity
- https://youtu.be/VXLtKlmtrvM Protected characteristics
- Understanding unconscious bias | The Royal Society – YouTube Unconscious bias
- https://youtu.be/1I3wJ7pJUjg?feature=shared White privilege
BAPO is launching some EDI quote cards to raise awareness about the lived experience, barriers and enablers for some members of the P+O community, we want to challenge perceptions and bias and open up the conversation about inclusive environments in P+O.
If you would like to share your experience, please complete the MS form using the button below:
The learner’s welcome pack has been designed for practice educators to edit and share with learners about embarking on practice-based placements. It is a document for practice educators to collate all the relevant information needed for learners for easy reference and can be used as a source of support for learners. The aim is to standardise the way you as the learner receive information about placement and raise awareness of and promote open conversations about the challenges of learning, mental health and wellbeing including stress management, and EDI, including content on reasonable adjustments to contribute towards an inclusive placement experience. If you have not received a copy of this from your practice educator, you could download it and work with your practice educator to make sure you gather all of the essential information required for your placement. This pack is best viewed electronically as there are clickable links and resources throughout.
The placement form provides a tool for capturing key information about you as an individual learner, your approach to learning and your individual learning support needs, including any required reasonable adjustments. The completed form can be shared with your practice educator before your placement commences, to allow suitable preparations to be made to support you to maximise the learning opportunities from your practice- based education.